Exclusives
Supplement Industry Contributes $122 Billion To U.S. Economy
Collectively, industry contributed more than 750,000 jobs nationwide, according to economic report.

By: Sean Moloughney
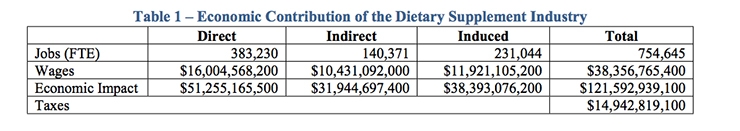
More than two-thirds of American adults take dietary supplements each year, and according to a new economic impact report funded by the Council for Responsible Nutrition (CRN), the dietary supplement industry contributes $121.6 billion to the U.S. economy (about 0.68% of GDP), creates 754,645 jobs nationwide, and pays $38.4 billion in wages. Additionally, the industry contributes nearly $15 billion in business taxes—federal and state—not including taxes collected on product sales.
This economic impact report was produced by John Dunham and Associates on behalf of CRN. The results are accessible here and provide data on a national basis, as well as state-by-state and by congressional district.
According to CRN President & CEO Steve Mister, the dietary supplement industry is robust, “and this new economic analysis further demonstrates the important and positive impact our industry has on people’s lives. We’re releasing this report in conjunction with our annual fly-in on Capitol Hill, where more than 60 dietary supplement industry executives from 40 companies will share this information with elected officials. We urge all companies in the industry to do the same on national, state and local levels.”
The statistics are based on the total overall economic impact from the industry, which combines direct contributions (those that are solely attributable to the dietary supplement industry), indirect contributions (those that result from dietary supplement industry firms purchasing goods and services from other industries) and induced effects (which economists refer to as the multiplier effect of an activity—in this case, resulting from the dietary supplement industry).
Mr. Mister added, “With the completion of this new report, CRN can demonstrate a trifecta of data about dietary supplements and the people who take them. Here’s what we know: more than 150 million Americans take dietary supplements for the health benefits they provide; supplements offer tremendous potential for societal healthcare cost savings; and the industry makes vital contributions to the economy at large. What’s good for your health is also very good for America’s wallet.”
Report Details
The 2016 Economic Impact of the Dietary Supplement Industry report measured the combined impact of the manufacturing, retail, wholesale, ingredient suppliers, and direct-selling industries to the U.S. economy in 2016. The analysis used standard econometric models first developed by the U.S. Forest Service, and now maintained by IMPLAN Group, LLC. Data came from industry sources, government publications, Dun & Bradstreet, Inc, and Infogroup.
The industry is defined to include not only the production of dietary supplement products, but dietary supplement wholesaling and retailing. The production process (as defined in this study) begins with ingredients (e.g., fish oils, herbs and botanicals) being purchased by manufacturers from suppliers. Ingredients are then extracted, blended, formulated and packaged by the manufacturer.
Once dietary supplements have been produced, they enter the second tier of the industry: the wholesaling tier. Wholesalers are involved in the transportation of dietary supplements from either the producers or from a bonded warehouse operated by importers, and the storage of products for a limited period of time. The third tier of the industry is retailing, either through brick-and-mortar sales (as in the case of a grocery store or pharmacy), or sales from direct sales companies (Amway and Nu Skin, for example).
According to the report, the dietary supplement industry is a dynamic part of the U.S. economy, accounting for about $121.59 billion in total economic output, or roughly 0.68% of GDP, based on 2015 GDP of $18.2 trillion. Dietary supplement manufacturers, ingredient suppliers, wholesalers, direct sellers, and retailers directly employed 383,230 Americans in 2016. These workers earned over $16 billion in wages and benefits. When indirect and induced impacts are taken into account, the dietary supplement industry is responsible for: 754,645 jobs in the U.S. and $38.36 billion in wages, as well as $14.94 billion in Federal, state and local taxes—not including state and local sales taxes imposed on dietary supplements.
According to the report, 962 facilities comprise the manufacturing component of the dietary supplement industry; combined with the ingredient suppliers, the production sector employs approximately 53,589 people.
Additionally, the dietary supplement industry is directly responsible for approximately 5,408 jobs in the wholesaling sector. Finally, the third tier of the industry directly sells products to the consumer. For this analysis, the retail tier is assumed to consist of firms in the following industries: supermarkets, nutrition stores, health food markets, mail-order catalogues, websites, direct-sellers, pharmacies, warehouse stores, and other miscellaneous retail stores. The dietary supplement industry is directly responsible for approximately 324,233 jobs in the retailing sector.
Other indirect firms produce and sell a broad range of items including machinery, tools, parts, and other materials needed to produce dietary supplements. In addition, indirect firms can provide a range of services, including personnel, financial, advertising, consulting, and/or transportation. Finally, a number of people are employed in government enterprises responsible for the regulation of the dietary supplement industry. All told, the report estimated that the dietary supplement industry is responsible for 140,371 indirect jobs. Indirect firms generate about $31.94 billion in economic activity.
The economic impact analysis was developed by JDA based on data provided by CRN, Nutrition Business Journal (NBJ), Dun & Bradstreet, Inc. (D&B, Inc.), Infogroup, and Federal and state governments. The analysis utilizes the IMPLAN Group, LLC’s model in order to quantify the economic impact of the dietary supplement industry on the economy of the U.S. The model adopts an accounting framework through which the relationships between different inputs and outputs across industries and sectors are computed. This model can show the impact of a given economic decision—such as a factory opening or operating a sports facility—on a pre-defined, geographic region. It is based on the national income accounts generated by the U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA).